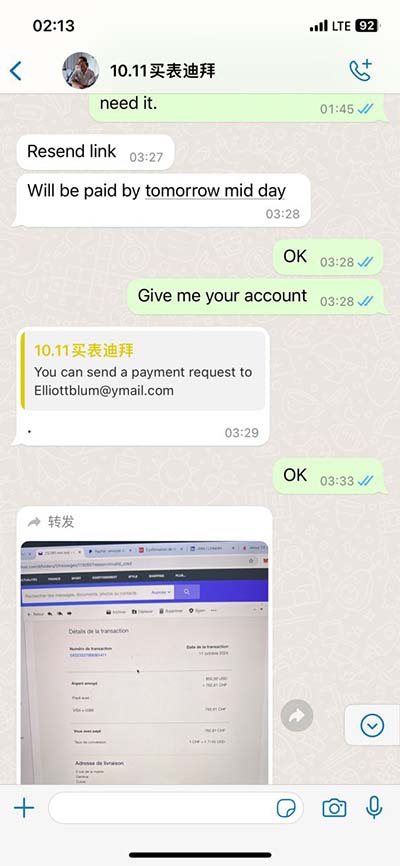
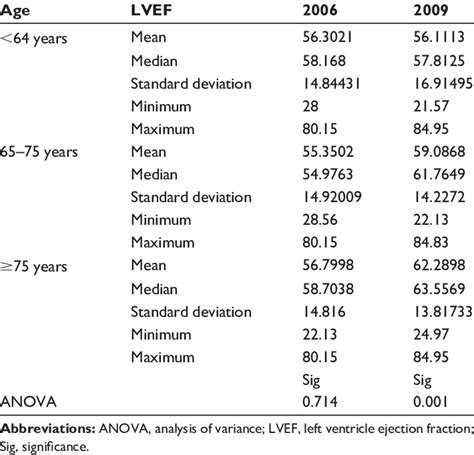
lv ejection fraction meaning | left ventricular ejection fraction echo lv ejection fraction meaning A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection fraction is usually 40% or less. Abstract. Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
0 · lvef by age
1 · lvef 35 40 meaning
2 · lv ejection fraction 60
3 · left ventricular ejection fraction lvef
4 · left ventricular ejection fraction echo
5 · ejection fraction mild moderate severe
6 · ejection fraction heart failure
7 · echocardiogram ejection fraction normal range
Zoning Map – October 11, 2016 (PDF) © Copyright 2024 | site by Seth Graham Computers & Design Powered By WordpressWordpress
Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how . Ejection fraction typically refers to the left side of the heart. It shows how much oxygen-rich blood is pumped out of the left ventricle to most of the body’s organs with each contraction. LVEF helps determine the severity of dysfunction on the left side of the heart. Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent means that 60 percent of the total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pushed out with each heartbeat. Ejection fraction is a test that's used to determine the percentage of blood that leaves your left ventricle each time your heart beats.
A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection fraction is usually 40% or less. Left ventricular measures how much blood gets pumped from the left ventricle with each contraction. Typically, ejection fraction refers to left ventricular. Right ventricular ejection fraction measures how much blood is pumped out of the right side of the heart, to the lungs. What are the tests used to measure ejection fraction? Ejection fraction (EF) measures the amount of blood pumped out of your heart's lower chambers, or ventricles. It's the percentage of blood that leaves your. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume).
100. EF = ejection fraction. The term "ejection fraction" refers to the percentage of blood that's pumped out of a filled ventricle with each heartbeat. Ejection fractions are calculated during an echocardiogram.
lvef by age
Ejection fraction refers to how much blood the heart pumps out during a contraction. An abnormal ejection fraction can be a sign of heart failure. Some people might need treatment to. Ejection fraction typically refers to the left side of the heart. It shows how much oxygen-rich blood is pumped out of the left ventricle to most of the body’s organs with each contraction. LVEF helps determine the severity of dysfunction on the left side of the heart. Ejection fraction (EF) is a measurement, expressed as a percentage, of how much blood the left ventricle pumps out with each contraction. An ejection fraction of 60 percent means that 60 percent of the total amount of blood in the left ventricle is pushed out with each heartbeat. Ejection fraction is a test that's used to determine the percentage of blood that leaves your left ventricle each time your heart beats.
A left ventricle (LV) ejection fraction of about 50% to 70% is categorized as normal. A mildly reduced LV ejection fraction is usually between 41% and 49%. A reduced LV ejection fraction is usually 40% or less. Left ventricular measures how much blood gets pumped from the left ventricle with each contraction. Typically, ejection fraction refers to left ventricular. Right ventricular ejection fraction measures how much blood is pumped out of the right side of the heart, to the lungs. What are the tests used to measure ejection fraction?
Ejection fraction (EF) measures the amount of blood pumped out of your heart's lower chambers, or ventricles. It's the percentage of blood that leaves your. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in relation to the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of diastole (end-diastolic volume).100. EF = ejection fraction.
The term "ejection fraction" refers to the percentage of blood that's pumped out of a filled ventricle with each heartbeat. Ejection fractions are calculated during an echocardiogram.
lvef 35 40 meaning
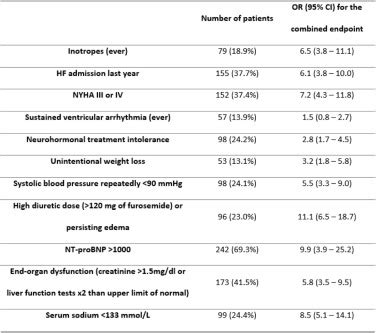
lv ejection fraction 60
left ventricular ejection fraction lvef
Après avoir eu recours à leurs interventions de chirurgie esthétique, certains youtubeurs assument publiquement l'opération subie. Caméra embarquée, certains par souci de transparence envers .
lv ejection fraction meaning|left ventricular ejection fraction echo