lv crypt | left ventricular myocardial mass lv crypt Abstract. Aims: Left ventricular (LV) myocardial crypts are considered a subtle . The ST elevation is defined by ≥1 mm in at least two adjacent leads. The ST changes seen in early repolarization are different than the ST changes seen with acute ischemia/infarction that are due to current flow, called "injury current," across the area between ischemic and non-ischemic myocardium. 26
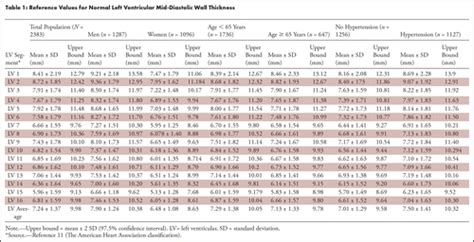
0 · normal Lv wall thickness
1 · myocardial wall thickness
2 · myocardial crypts
3 · left ventricular myocardial mass
4 · hypokinesis and myocardial thinning
5 · Lv perfusion is abnormal
6 · Lv end diastolic septal thickness
7 · Lv diverticulum vs aneurysm
What is the definition of low voltage, medium voltage, high voltage and extra high voltage? Definitions vary somewhat but a general guide to the voltage categories are as follows: Low Voltage (LV): up to 1000V. Medium Voltage (MV): between 1000 V and 45 kV. High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV.
The first consecutive series of HCM mutation carriers systematically investigated . Abstract. Aims: Left ventricular (LV) myocardial crypts are considered a subtle .
These “architectural abnormalities” of the left ventricle (LV) occur particularly in the .
LV outpouchings commonly include aneurysms, pseudoaneurysms, and . Left ventricular myocardial crypts were identified more commonly among .
Myocardial Crypts. Myocardial crypts (or clefts) have been defined as discrete V . Myocardial clefts (MCs) are narrow, deep invaginations within the myocardium, .
normal Lv wall thickness
A cleft or crypt can be described as a discrete, approximately “V” shaped .

The first consecutive series of HCM mutation carriers systematically investigated by CMR 6 demonstrated an 81% prevalence of so-called crypts in the inferoseptal LV . Abstract. Aims: Left ventricular (LV) myocardial crypts are considered a subtle marker of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. However, crypts have also been observed in .
These “architectural abnormalities” of the left ventricle (LV) occur particularly in the septum and inferior (posterior) right ventricular (RV) insertion point and had been observed at .
LV outpouchings commonly include aneurysms, pseudoaneurysms, and diverticula. Myocardial clefts/crypts have uncertain clinical significance and may be in some .
myocardial wall thickness
Left ventricular myocardial crypts were identified more commonly among genotype-positive/phenotype-negative (G+ P−) patients with HCM (61%) compared with 261 patients .
Myocardial Crypts. Myocardial crypts (or clefts) have been defined as discrete V-shaped extensions of the blood pool inserting more than 50% into the compact myocardial wall . Myocardial clefts (MCs) are narrow, deep invaginations within the myocardium, localized predominantly in the basal inferior septum and left ventricular (LV) free walls . The .
A cleft or crypt can be described as a discrete, approximately “V” shaped fissure extending into but confined by the myocardium, with a tendency to narrow or occlude in .Rapid advances in cardiac computed tomography (CT) have enabled the characterization of left ventricular (LV) myocardial diseases based on LV anatomical morphology, function, density, .
Left ventricular (LV) myocardial crypts are considered a subtle marker of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. However, crypts have also been observed in seemingly healthy . The first consecutive series of HCM mutation carriers systematically investigated by CMR 6 demonstrated an 81% prevalence of so-called crypts in the inferoseptal LV .
Abstract. Aims: Left ventricular (LV) myocardial crypts are considered a subtle marker of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. However, crypts have also been observed in . These “architectural abnormalities” of the left ventricle (LV) occur particularly in the septum and inferior (posterior) right ventricular (RV) insertion point and had been observed at . LV outpouchings commonly include aneurysms, pseudoaneurysms, and diverticula. Myocardial clefts/crypts have uncertain clinical significance and may be in some . Left ventricular myocardial crypts were identified more commonly among genotype-positive/phenotype-negative (G+ P−) patients with HCM (61%) compared with 261 patients .
myocardial crypts
Myocardial Crypts. Myocardial crypts (or clefts) have been defined as discrete V-shaped extensions of the blood pool inserting more than 50% into the compact myocardial wall . Myocardial clefts (MCs) are narrow, deep invaginations within the myocardium, localized predominantly in the basal inferior septum and left ventricular (LV) free walls . The .

A cleft or crypt can be described as a discrete, approximately “V” shaped fissure extending into but confined by the myocardium, with a tendency to narrow or occlude in .Rapid advances in cardiac computed tomography (CT) have enabled the characterization of left ventricular (LV) myocardial diseases based on LV anatomical morphology, function, density, .
versace perfume amazon fake
how to spot fake clinique happy heart perfume
Low Voltage (LV) Solar Array is an IC Machine used to generate EU from the sun. It is the equivalent of 8 Solar Panels. One LV Solar Array produces 8 EU/t, which is 160 EU per second, or 104,400 EU per day. It is a low voltage device. LV Solar Arrays are the cheapest out of the three Solar Arrays (The others being MV and HV Solar Array's).
lv crypt|left ventricular myocardial mass