lv esv | esv heart meaning lv esv End-diastolic volume is the amount of blood in the heart’s left ventricle just before the heart contracts. It affects how well the heart pumps . A simple idea making a brilliant game. You have a calculator and you need to achieve a certain number with limited moves and buttons. Use you imagination and brain to solved all the levels. You can use some hints to know in which order you need to press the buttons in order to get the answers.
0 · what is Lv edv bp
1 · normal edv and esv values
2 · esv heart meaning
3 · Lv esv bp normal range
4 · Lv esv 2d teichholz
5 · Lv edvi
6 · Lv edv normal range
7 · Lv edv BP meaning
Calculus: Basic Concepts for High Schools: Author: L. V. Tarasov: Edition: revised: Publisher: Mir Publishers, 1982: ISBN: 0828522782, 9780828522786: Length: 184 .
The percentage portions of papillary muscle and trabeculae to LV end-diastolic volume (EDV) and LV mass (LVM) were 11.9 ± 5.6% and 20.2 ± 4.3%, respectively, significantly affecting disease .
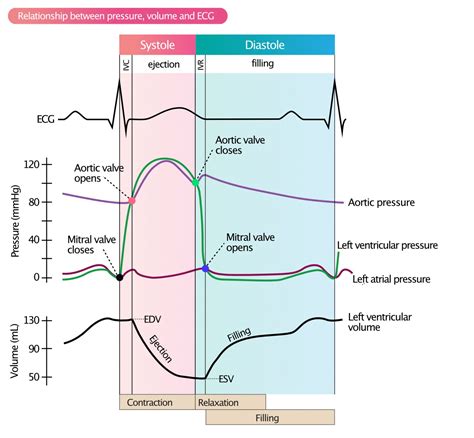
End-diastolic volume is the amount of blood in the heart’s left ventricle just before the heart contracts. It affects how well the heart pumps .
The percentage portions of papillary muscle and trabeculae to LV end-diastolic volume (EDV) and LV mass (LVM) were 11.9 ± 5.6% and 20.2 ± 4.3%, respectively, significantly affecting disease . End-systolic volume (ESV) is the volume of blood in the ventricle at the end of systole. It is used to assess cardiac function and calculate stroke volumes and ejection . End-diastolic volume is the amount of blood in the heart’s left ventricle just before the heart contracts. It affects how well the heart pumps blood and can be altered by various .
End-systolic volume (ESV) is the lowest volume of blood in a ventricle at any point in the cardiac cycle. Learn how ESV is measured, what factors affect it, and what it means for cardiac function. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in .Learn how preload, afterload and inotropy affect stroke volume (SV), the amount of blood ejected per beat by the ventricle. Find out how changes in these factors alter the ventricular end .Ejection fraction (EF) is the percentage of blood ejected by the left ventricle during systole. EF is affected by preload, afterload, and ventricular volume, and can be reduced by various .
what is Lv edv bp
The end of LV filling occurs when the aortic valve closes and represents the LV end-systolic pressure (LVESP) and LVESV (E). This point marks the beginning of diastole and results in . LV volumes and mass both rise in adolescence and decline with age. EF showed a rapid decline in adolescence compared to changes throughout adulthood. These findings .Learn how to measure LV size and function using 2DE or 3DE methods, and compare normal values for ejection fraction, strain, and regional wall motion. This document also covers RV .
normal edv and esv values
The percentage portions of papillary muscle and trabeculae to LV end-diastolic volume (EDV) and LV mass (LVM) were 11.9 ± 5.6% and 20.2 ± 4.3%, respectively, significantly affecting disease . End-systolic volume (ESV) is the volume of blood in the ventricle at the end of systole. It is used to assess cardiac function and calculate stroke volumes and ejection .
End-diastolic volume is the amount of blood in the heart’s left ventricle just before the heart contracts. It affects how well the heart pumps blood and can be altered by various .End-systolic volume (ESV) is the lowest volume of blood in a ventricle at any point in the cardiac cycle. Learn how ESV is measured, what factors affect it, and what it means for cardiac function.
Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) is the central measure of left ventricular systolic function. LVEF is the fraction of chamber volume ejected in systole (stroke volume) in .Learn how preload, afterload and inotropy affect stroke volume (SV), the amount of blood ejected per beat by the ventricle. Find out how changes in these factors alter the ventricular end .Ejection fraction (EF) is the percentage of blood ejected by the left ventricle during systole. EF is affected by preload, afterload, and ventricular volume, and can be reduced by various .
The end of LV filling occurs when the aortic valve closes and represents the LV end-systolic pressure (LVESP) and LVESV (E). This point marks the beginning of diastole and results in . LV volumes and mass both rise in adolescence and decline with age. EF showed a rapid decline in adolescence compared to changes throughout adulthood. These findings .
gucci hat shirt
esv heart meaning
121 were here. Camaradas Mexican-Italian Kitchen is the most unique food truck in Las Vegas. We blend traditional M
lv esv|esv heart meaning